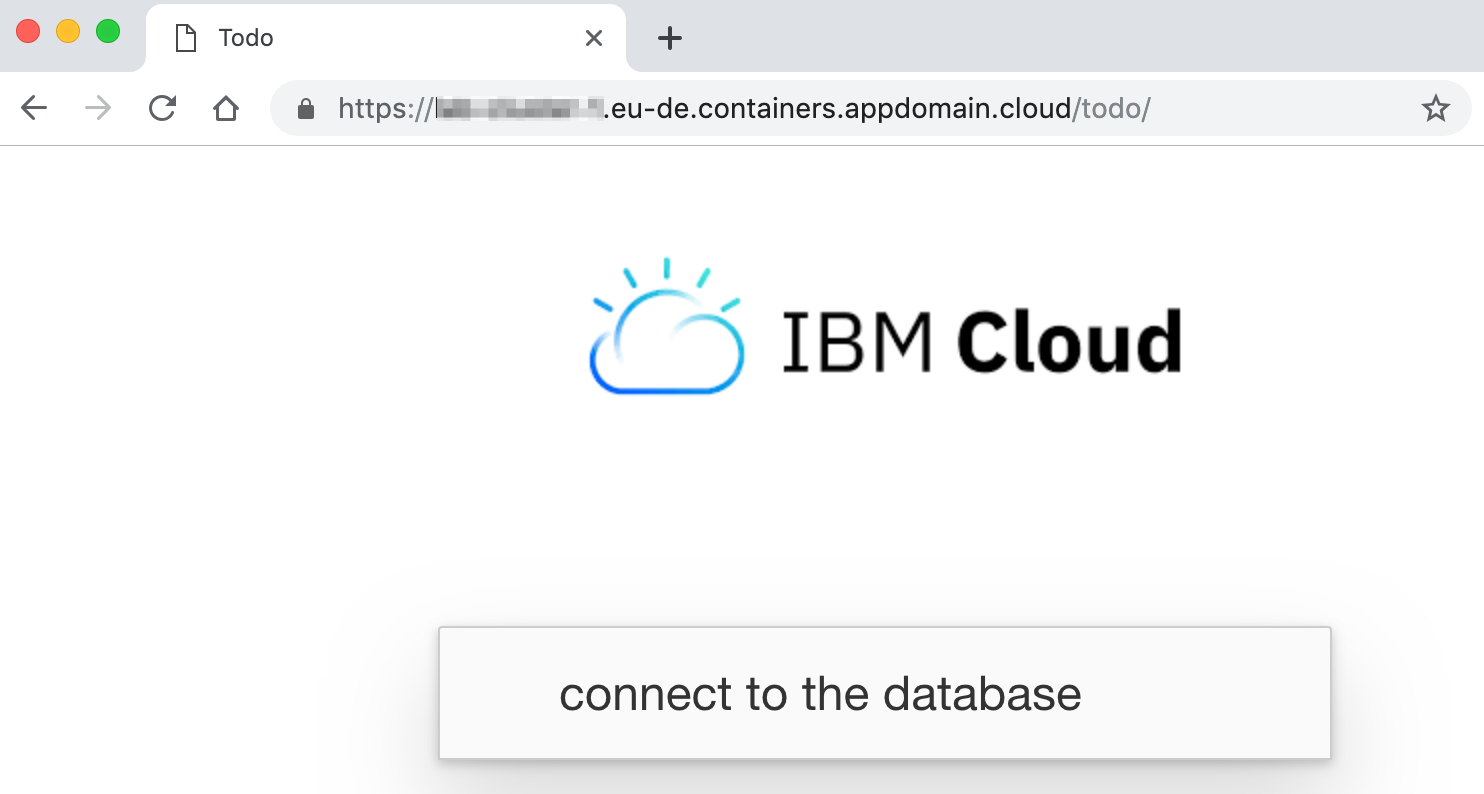
Use a Kubernetes Secret to connect to a managed Database service.
The initial version of the application uses an in-memory database to store the todo. Yet, the web application can be configured to store the todo in either a Cloudant or a Mongo DBaaS. We will use a Cloudant DB to demonstrate how to connnect the web app to the Cloudant service using the Kubernetes Secret.
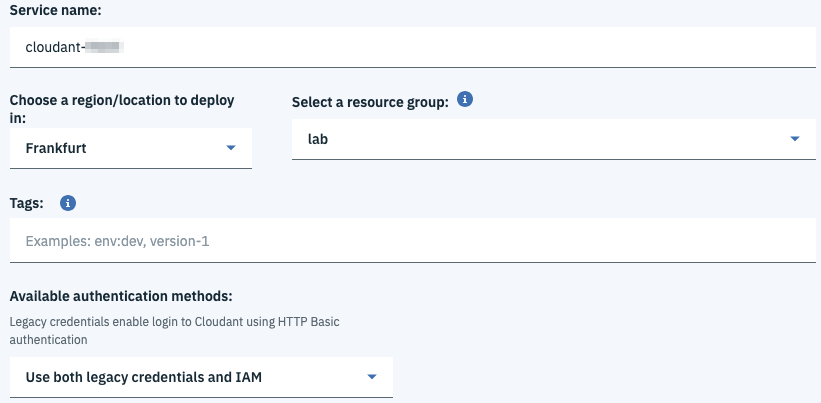
Create an instance of Cloudant and its credentials
Go to the Cloud Services Catalog
To see all the available services in the catalog using the cli:
ibmcloud catalog service-marketplaceSelect the service Cloudant
add your lastname as a Tag
Create an instance of the service with the plan Lite
Click create. It will take a few minutes to provision the service.
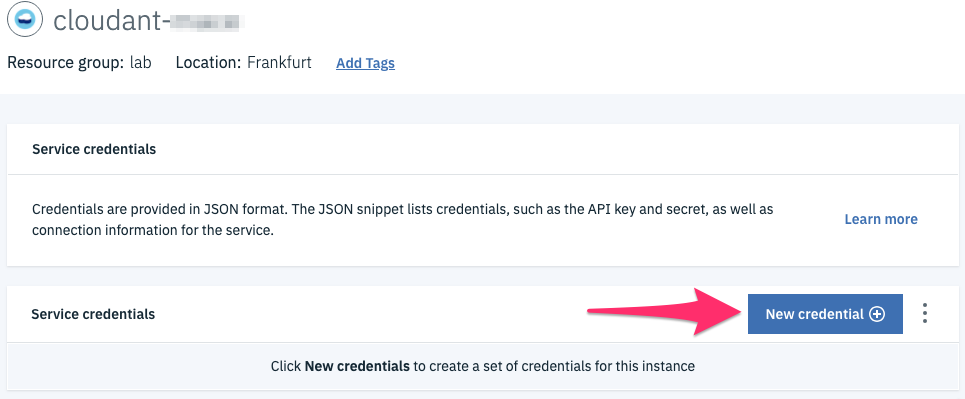
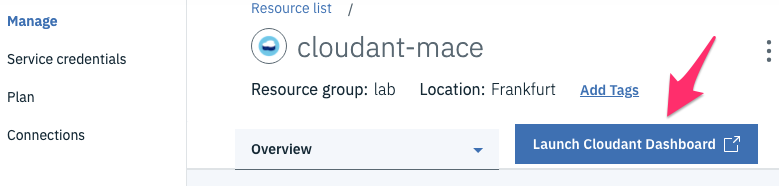
Click on the hamburger menu, select Resource List, and select the cloudant instance you just created.
Create the credentials to access the service.
select Service Credentials
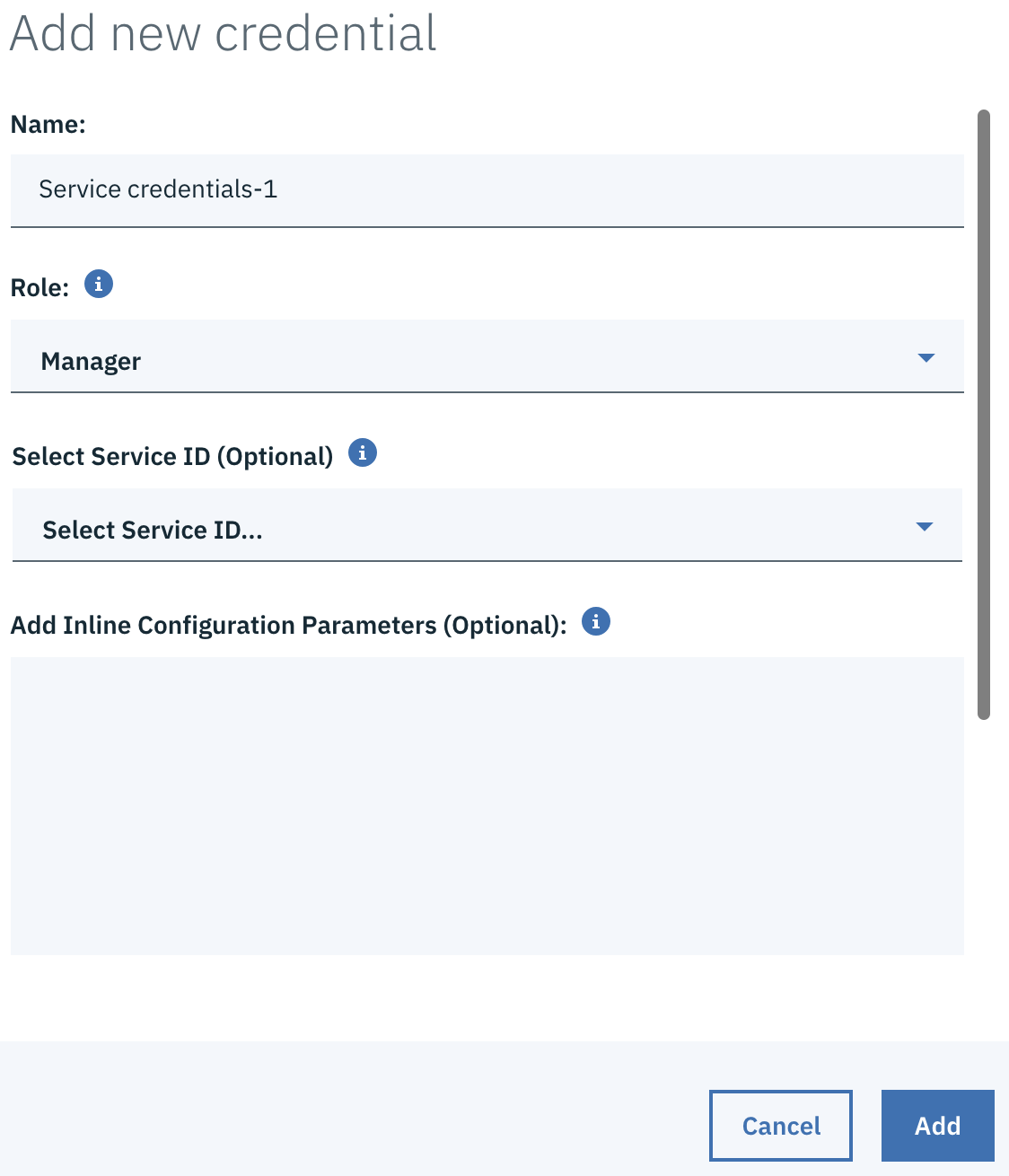
Click New Credentials and keep all the default options
Duplicate the file
~/todo/credentials.template.envin the root folder to a new filecredentials.envEdit the file
credentials.envand fill out the value for both CLOUDANT_USERNAME and CLOUDANT_APIKEY from the generated credentials above. Make sure you uncomment those 2 linesOptional: Create an instance of a service using the CLI instead of the Console.
ibmcloud resource service-instance-create <service_instance_name> <service_name> <service_plan_name> <location>Example:
ibmcloud resource service-instance-create todo-cloudant cloudant lite eu-deOptional: Verify you see the new instance created using the CLI
ibmcloud resource service-instances
Create the Kubernetes Secret
Unless you have created a new namespace, we will use the namespace default in this lab. To find the list of Kubernetes namespaces:
kubectl get namespacesOutput:
NAME STATUS AGE default Active 7d ibm-system Active 7d kube-system Active 7dCreate the secret used by the application to obtain service credentials:
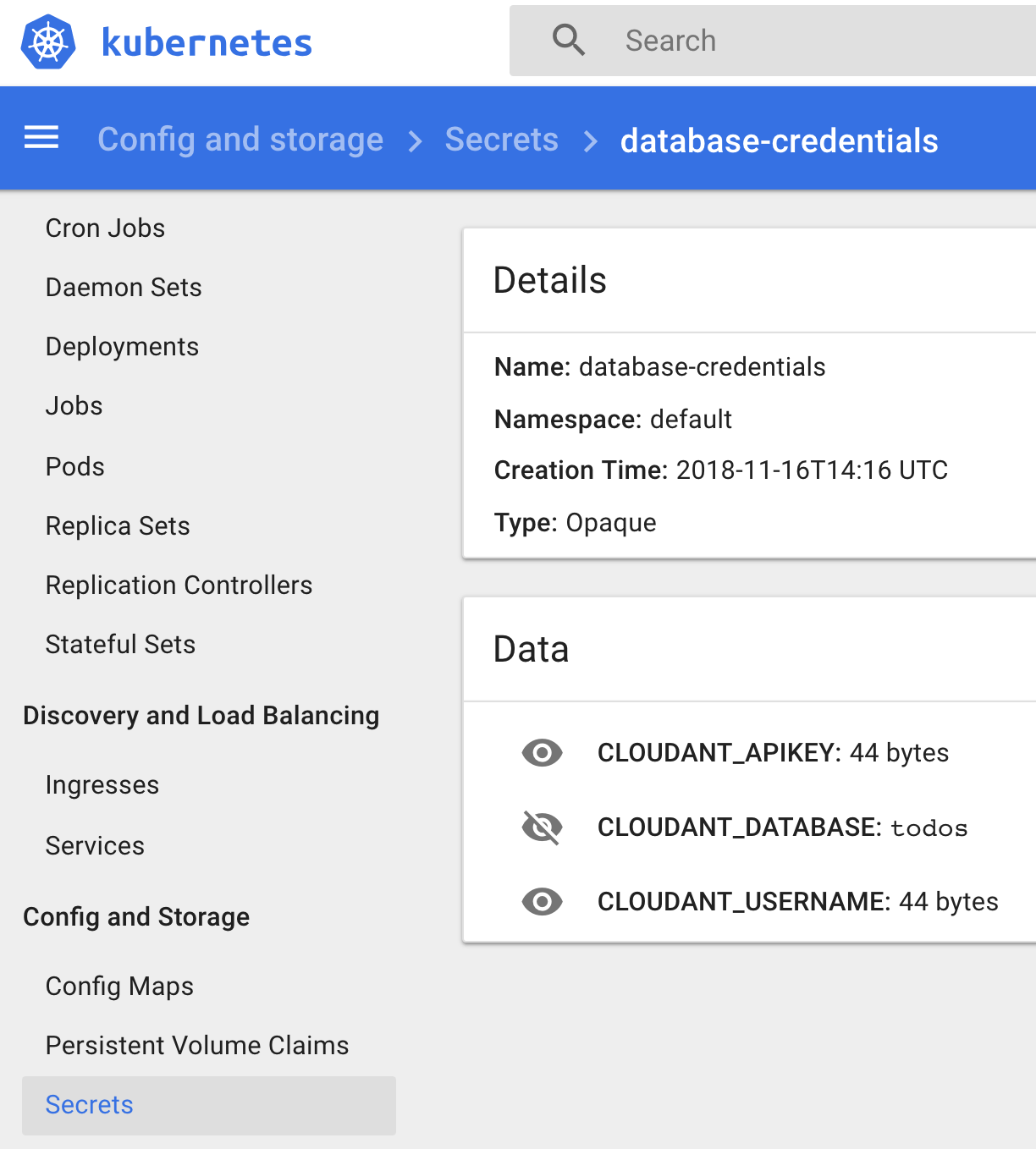
kubectl create secret generic database-credentials --from-env-file=credentials.envResult:
secret/database-credentials created
Control that your secret was successfully created
kubectl get secretsYou can view the secret in the Kubernetes Dashboard
Redeploy the app
Modify the YAML to uncomment the last 3 lines of the Deployment section as of envFrom.
Your YAML file should look as follows:
--- # Application to deploy apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: mytodos spec: replicas: 2 # tells deployment to run 2 pods matching the template selector: matchLabels: app: mytodos template: # create pods using pod definition in this template metadata: labels: app: mytodos tier: frontend spec: containers: - name: mytodos image: <region>.icr.io/<namespace>/todo-<lastname>:1.0 imagePullPolicy: Always resources: requests: cpu: 250m # 250 millicores = 1/4 core memory: 128Mi # 128 MB limits: cpu: 500m memory: 384Mi envFrom: - secretRef: name: database-credentialsUpdate the application with this new configuration
kubectl apply -f ingress-tls-deploy.yamlCreate a new todo in the web app.
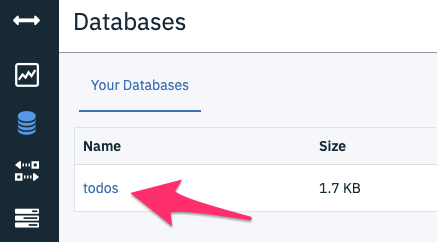
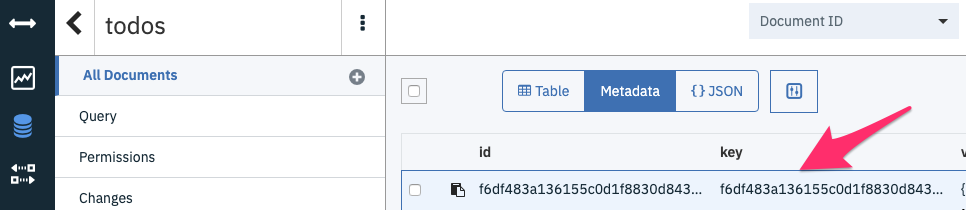
Check the Cloudant Dashboard to validate this new todo has been persisted in the DB.